DHHS → MeCDC → Disease Surveillance → Epidemiology → Tuberculosis
Tuberculosis
Note to Healthcare Providers: Please use the new TB suspect and case report form for all inactive (formerly LTBI) and active TB reporting.
I want to know:
What is Tuberculosis (TB)?

How does Tuberculosis (TB) spread?

Symptoms of Tuberculosis (TB)

Tuberculosis Testing and Treatment
Tuberculosis Control in Maine
Resources:

What should I do if...?

Resources for Patients

Resources for Health Care Providers

Resources for Congregate Settings
What Is Tuberculosis?
Tuberculosis (TB) is an infection caused by a bacterium called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It usually affects the lungs. However, other parts of the body can also be affected, like the kidney, spine, and brain. Not everyone infected with TB gets sick.
Inactive TB (formerly LTBI) and Active TB Disease
Not everyone who gets infected by TB germs becomes sick. As a result, there are two TB-related conditions: Inactive TB (formerly latent TB infection, LTBI) and Active TB disease. Download the Inactive TB (LTBI) vs Active TB handout (PDF).
Inactive TB
In most people who breathe in TB bacteria and become infected, the body fights the bacteria to stop them from growing. The TB germs are alive but inactive. These people have inactive TB. They:
- Have no symptoms.
- Do not feel sick.
- Cannot spread TB bacteria to others.
- Usually have a positive skin or blood TB test.
- May develop TB disease if they do not receive treatment for latent TB infection.
Treatment for inactive TB usually lasts 3 to 4 months. It is effective and safe.
Active TB Disease
If the body cannot stop TB germs from growing, the person develops active TB. These people have large amounts of active and growing TB germs in their body. People with active TB:
- Have symptoms and feel sick.
- May be able to spread the bacteria to other people.
Treatment for active TB usually lasts at least 6 to 12 months. It is effective and safe.
The risk of developing active TB is much higher for people with weakened immune systems, especially for those with HIV infection, than for people with normal immune systems.
How Does Tuberculosis Spread?
When someone with active TB disease of the lung coughs, sneezes, speaks, or sings, TB germs get into the air. People who share the same air space with this person may breathe these germs into their lungs. Sometimes the germs spread to other parts of the body. Anyone can get TB infection. People at greater risk are family members, friends, and coworkers or schoolmates who share the same air space with the person who has TB disease of the lungs.
Other people at increased risk include:
- People living or working in group settings.
- People who abuse drugs or alcohol.
- People with medical conditions such as diabetes, HIV infection, or certain types of cancer.
- People who are underweight.
- People coming from countries with high rates of TB.
TB does NOT spread by:
- Shaking someone's hand
- Sharing food or drink
- Touching bed linens or toilet seats
- Sharing toothbrushes
- Kissing
Symptoms of Tuberculosis
Symptoms of active TB depend on where in the body the TB bacteria grow. TB bacteria usually grow in the lungs. TB disease in the lungs may cause symptoms like:

A bad cough that last 3 weeks or longer

Pain in the chest
Coughing up blood or sputum (phlegm from deep in the lungs)

Weakness or feeling very tired
Weight loss

No appetite

Fever and chills
Sweating at night
TB usually grows in the lungs but it can also grow in other parts of the body. This includes the brain, the kidneys, and the spine. Symptoms can change depending on what part of the body is affected.
Tuberculosis Testing and Treatment
There are two types of tests for TB infection, the TB blood test and the TB skin test. Your health care provider can help decide what test is right for you. Getting tested and treated for TB helps to protect you, your family and friends, and your community. No matter which test type you use, you can use this information to understand your results. Talk to your health care provider to understand more and find out what your next steps are.
A Positive Test for TB Infection (+)
This result means you have TB germs in your body.
Your health care provider will do other tests to find out if you have inactive TB or active TB. These tests may include a chest x-ray and a test of sputum you cough up from your lungs.
Tell your health care provider if you received a TB vaccine. TB blood tests are best for people who received the bacille Calmette-Guerin (BCG) TB vaccine. Unlike the TB skin test, TB blood tests are not affected by BCG vaccination.
A Negative Test for TB Infection (-)
This result means you most likely do not have inactive TB or active TB.
Your health care provider may do more tests if:
- You have symptoms of active TB, like coughing, chest pain, fever, weight loss, or feeling very tired.
- You have HIV infection.
- You had recent exposure to TB germs.
Treatment Is Important
TB germs can live in your body for years without causing symptoms. If you have inactive TB, treating it is the best way to protect you, your family, and your friends from getting sick with active TB.
If a health care provider diagnoses you with TB disease, you can be treated with medicine. You need to take and finish all of your TB medicine as directed by your health care provider. This will help you feel better and prevent other people from getting sick.

Directly Observed Therapy (DOT)
The best way to remember to take your medicines for active TB is through directly observed therapy (DOT). Through DOT, you meet with a public health nurse every day or several times a week, either in-person or virtually. The public health nurse will make sure that the TB medicines are working as they should.

Tuberculosis Control in Maine
About TB Control in Maine
The TB Control Program provides surveillance of active TB throughout Maine. The TB Controller takes referrals from health care providers in Maine for patients with suspected or diagnosed active TB.
The TB Control Program has TB consultants around the state who are available to support diagnosis and treatment of active TB and inactive TB. TB consultants are private, board certified pulmonologists or infectious disease physicians. The TB Control Program can connect you with the consultant closest to you.
Maine's TB Control Program can help pay for medication to treat active TB and inactive TB. Maine CDC's Public Health Nurses help with ongoing case management, including directly observed therapy (DOT). They can also help with TB skin test training workshops.
Contact Maine CDC TB Control Program:
TB Preventive Treatment Referral AND 24/7 Disease Reporting Hotline: 1-800-821-5821
Disease Reporting and Consultation Email (not secure - do not send patient information): disease.reporting@maine.gov
Tuberculosis Data
What Should I Do If...
I was exposed to a person diagnosed with TB?
I found out that I am a close contact of someone with TB. What should I do?
- Only people with active TB disease of the lungs can spread TB bacteria to others.
- Not everyone who gets exposed to TB bacteria gets infected.
- a bad cough that lasts 3 weeks or longer
- pain in the chest
- coughing up blood or sputum
- weakness or feeling very tired
- weight loss
- no appetite
- chills or fever
- sweating at night
Download the I was exposed to a person diagnosed with tuberculosis. What now? (PDF) checklist.
I have TB Symptoms?
I have TB symptoms. What should I do?
- Only people with active TB disease of the lungs can spread TB bacteria to others.
- Not everyone who gets exposed to TB bacteria gets infected.
Download the I have symptoms of tuberculosis. What Now? (PDF) checklist.
I had a positive TB skin or blood test?
I had a positive tuberculosis skin or blood test. What should I do?
Download the I had a positive TB skin or blood test. What now? (PDF) checklist.
I have confirmed TB Disease?
I have active TB disease. What should I do?
Download the I have tuberculosis (TB) disease. What now? (PDF) checklist.
Resources
Resources for Patients

Tuberculosis Fact Sheet (PDF) | عربي | Français (PDF) | Kreyòl Ayisyen (PDF) | Lingala (PDF) | Português (PDF) | Soomaali (PDF) | Español (PDF) | Tiếng Việt (PDF)
Tuberculosis: Inactive TB (LTBI) vs Active TB (PDF)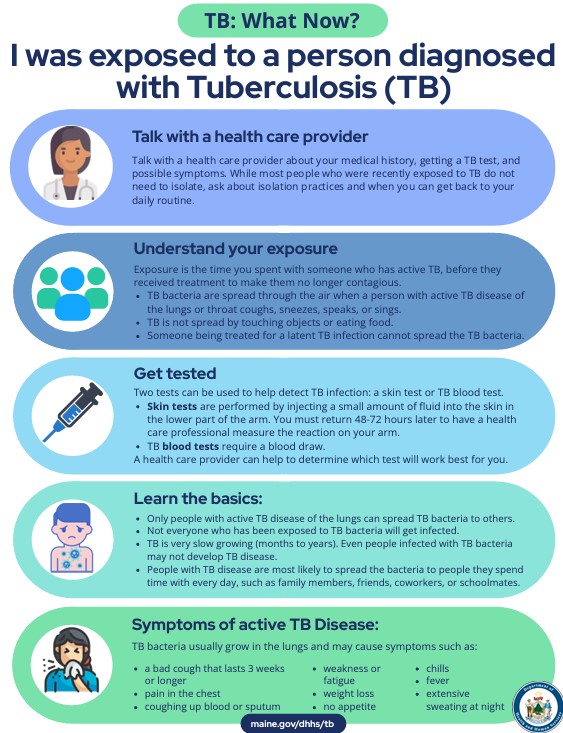
I was exposed to a person with TB. What now? (PDF)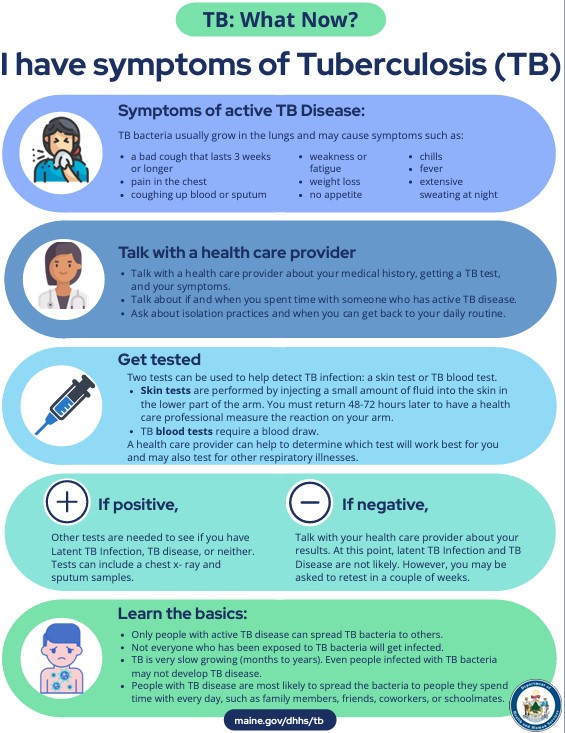
I have TB symptoms. What now? (PDF)
I had a positive TB skin or blood test. What now? (PDF)
I have TB disease. What now? (PDF)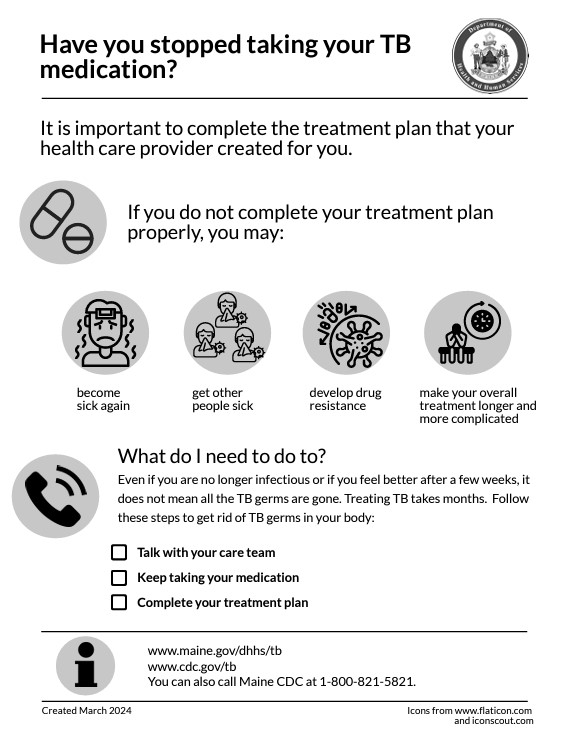
Have you stopped taking your TB medication? (PDF) | عربي | Français (PDF) | Kreyòl Ayisyen (PDF) | Lingala (PDF) | Português (PDF) | Soomaali (PDF) | Español (PDF) | Tiếng Việt (PDF)
Resources for Health Care Providers
TB Case or Suspect Report Form
Global Tuberculosis Institute - Tuberculosis Treatment Resources
Northern Light Health Webinar "Latent Tuberculosis for the Primary Care Clinician"
Maine CDC Webinar "Close contacts of persons diagnosed with TB disease: What primary care providers need to know" (MP4) | Presentation Slides (PDF)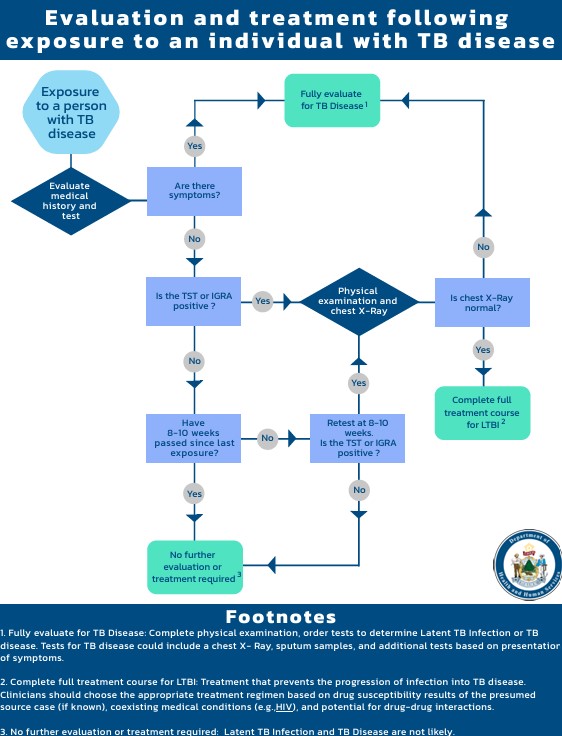
Evaluation and Treatment Following Exposure to an Individual with TB Disease Flowchart (PDF)
US CDC Tuberculosis Clinical Guidelines
About Drug Resistant Tuberculosis Disease - US CDC
US CDC Guidelines for Preventing the Transmission of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in Health Care Settings




